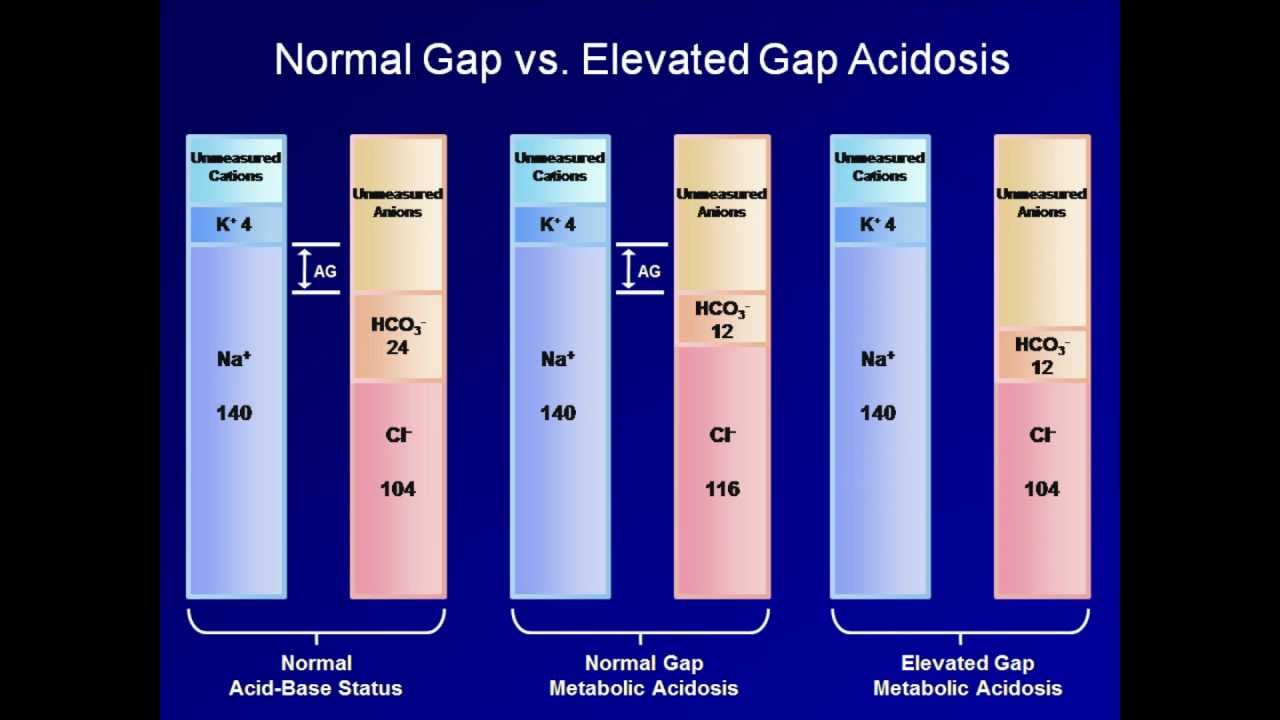
If the primary problem is direct loss of bicarbonate gain of chloride or decreased ammonia production the anion gap is within normal limits. Healthcare providers most commonly use anion gap to identify cases of metabolic acidosis when you have higher-than-normal amounts of.

Rosh Review Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis Medical Mnemonics
Overview and pathophysiology of renal tubular acidosis and the effect on potassium balance.

. A urine anion gap of more than 20 mEqL is seen in metabolic acidosis when the kidneys are unable to excrete NH4 such as in renal tubular acidosis. Bicarbonate 15-20 mEqL may increase the likelihood of recurrent DKA after stopping the insulin drip. Strong ions and the analysis of acid-base disturbances Stewart approach The delta anion gapdelta HCO3 ratio in patients with a high anion gap metabolic acidosis.
Metabolic acidosis increases insulin resistance. The delta anion gapdelta HCO3 ratio in patients with a high anion gap metabolic acidosis. The major pH buffer system.
Read more due to elevated blood lactate. The metabolic acidosis caused by RTA is a normal anion gap acidosis Types. Diabetes diabetic ketoacidosis Certain medicines and poisons.
If the primary problem is the accumulation of organic anions such as ketones or lactic. Lactic acidosis a condition where the body produces too much lactic acid 9 10 11. Principal causes include.
Hyperchloremic acidosis is a disease state where acidosis pH less than 735 develops with an increase in ionic chloride. An anion gap blood test checks the acid-base balance of your blood and if the electrolytes in your blood are properly balanced. Therefore persistent non-gap acidosis may delay transition off the insulin drip.
Lactic acidosis results from overproduction of lactate decreased. Anion gap is basically the difference between primary measured cations and anions in serum. A normal anion gap with a low HCO 3- 24 mEqL and high serum chloride indicates a non-anion gap hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis.
If the anion gap is normal just look at the bicarbonate. My opinion is that even a mild acidosis ie. A high anion gap test result may mean that you may have acidosis blood that is more acidic than normal.
8 to 16 if measured by older technique of flame photometry If AG 30 mmolL then metabolic acidosis invariably present. It compares the numbers of positively and negatively charged particles including sodium chloride and. Delta gap 15 - 12 3.
Hypercalcemia Hypercalcemia Hypercalcemia is a total serum calcium concentration 104 mgdL 260 mmolL or ionized serum calcium 52 mgdL 130 mmolL. Metabolic Acidosis is an acid-base. High anion gap metabolic acidosis made easy using the MUDPILES mnemonic.
Bicarbonate normal anion gap indicates a pure non-anion-gap metabolic acidosis NAGMA. Treatment of hypovolemia dehydration in children. Fluid and electrolyte disorders in adults.
Healthy subjects typically have a gap of 0 to slightly normal 10 mEqL. It was included in the classification of renal tubular acidoses as it is associated with a mild normal anion gap metabolic acidosis due to a physiological. An elevated anion gap strongly suggests the presence of a metabolic acidosis.
Understanding the physiological pH buffering system is important. PH may be markedly low or slightly. A normal anion gap with a low HCO 3.
A normal anion gap during metabolic acidosis may indicate a different set of causes. This is an indicator allowing us to give measure to the undetermined ions in plasma or serum. Metabolic acidosis is characterized by a primary reduction in serum bicarbonate HCO3- concentration a secondary decrease in the arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide PaCO2 of approximately 1 mmHg for every 1 mmoll fall in serum HCO3- concentration and a reduction in blood pH.
The list below details some potential causes of metabolic acidosis that is associated with a high anion gap. Learn the normal range for an anion gap and the formula that will determine if it is high or low. Learn the anion gap equation to calculate the level and apply it to a metabolic acidosis blood gas analysis.
Delta ratio 3 24 26 Delta ratio -15. As Ive mentioned previously on this blog the MUDPALES mnemonic for anion gap metabolic acidosis is one of the most successful medical mnemonics of all time. Metabolic acidosis is characterized by normal or high anion gap situations.
The normal anion gap varies with different assays but is typically 4 to 12mmolL if measured by ion selective electrode. Serum anion gap in conditions other than metabolic acidosis. Bicarbonate is a logical therapy for non-anion gap metabolic acidosis.
If the urine anion gap is zero or negative. Lactic acidosis is a high anion gap metabolic acidosis Metabolic Acidosis Metabolic acidosis is primary reduction in bicarbonate HCO3 typically with compensatory reduction in carbon dioxide partial pressure Pco2. High anion gap metabolic acidosis is a form of metabolic acidosis characterized by a high anion gap a medical value based on the concentrations of ions in a patients serum.
A decline in pH below this range is called acidosis an increase in this range is known as alkalosis. The effect is to cause a rise in plasma Cl- and the anion gap returns towards normal despite the persistence of the metabolic acidosis. This is the most common cause of metabolic acidosis.
Determination of the anion gap to evaluate for anion gap metabolic acidosis AGMA More on the anion gap above. If a high anion gap acidosis is present a delta ratio is calculated to help determine its cause and Winters formula is applied to determine whether respiratory compensation is present or whether there is a. Several types of metabolic acidosis occur grouped by their.
A model for the study of an anion gap acidosis not associated with hyperkalemia. This test measures the chemical balance in your blood. Acute kidney injury in adults.
Metabolic acidosis occurs when the body produces too much acid or when the kidneys are not removing enough acid from the body. Chloride excess eg normal. Potassium balance in acid-base disorders.
If AG 20-29mmolL then. Simple and mixed acid-base disorders. And Type B is lactic acidosis occurring in the context of normal tissue perfusion and adequate global tissue oxygenation.
For the urine anion gap the most prominently unmeasured cation is NH4. At presentation both types of acidosis may be present and the elevation in the anion gap will be less than expected for the degree of depression in the bicarbonate level resulting in Delta ratio. Acidosis may be caused by.
A less successful and admittedly less useful mnemonic exists for non-anion gap metabolic acidoses NAGMA which I learned as a resident. Bicarbonate 28 mM with a normal anion gap indicates a. An overview of types 1 2 and 4 is presented below type 3 is usually excluded from modern classifications.
A low anion gap test result may mean you have alkalosis blood that is less acidic than. Decreased anion gap is unrelated to metabolic acidosis but is caused by hypoalbuminemia decreased anions. Anion gap 145 104 26 AG 15 mEqL.
About the anion gap. Normal physiological pH is 735 to 745.

Pin On Anemia And Renal Nutrition

High Anion Gap Tool Medical Mnemonics Medical Laboratory Science Medical Knowledge

Usmle Wizard Metabolic Acidosis Uag Urine Anion Gap Negutive Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis Acidosis

The Classic Mnemonic Often Used To Remember The Causes Of Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis Is Mudpiles M Metha Medical Mnemonics Metabolic Acidosis Anion Gap

Metabolic Acidosis Metabolic Acidosis Acidosis Anion Gap

Dx Schema Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis The Clinical Problem Solvers Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis Acidosis

Respiratory Alkalosis Metabolic Acidosis Metabolic Alkalosis

Causes Of Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis Intellectual Property Of Knowmedge Com Mnemonic Goldmark G O L D M Medical Mnemonics Metabolic Acidosis Anion Gap

Pin On R1 Common Medical Emergency

Renal Physiology Acidosis And Alkalosis Flashcards Memorang

Case Internal Medicine Curriculum Internal Medicine Addisons Disease Metabolic Acidosis

Renal Tubular Acidosis Types And Pathology Creative Med Doses Renal Acidosis Hyperkalemia